
The treatment options
The treatment options for children suffering from epilepsy are neurostimulation and surgery. These treatments are designed to decrease the severity and frequency of seizures as well as speed up seizure healing. While these treatments have not been approved by the FDA, increasing numbers of research has shown their effectiveness. Children can also undergo surgery, such as hemispherectomy. This removes the part of the brain that is responsible for seizures. The procedure can stop seizures in children but is associated with risks, including reduced motor function, cognitive function, and behavior problems.
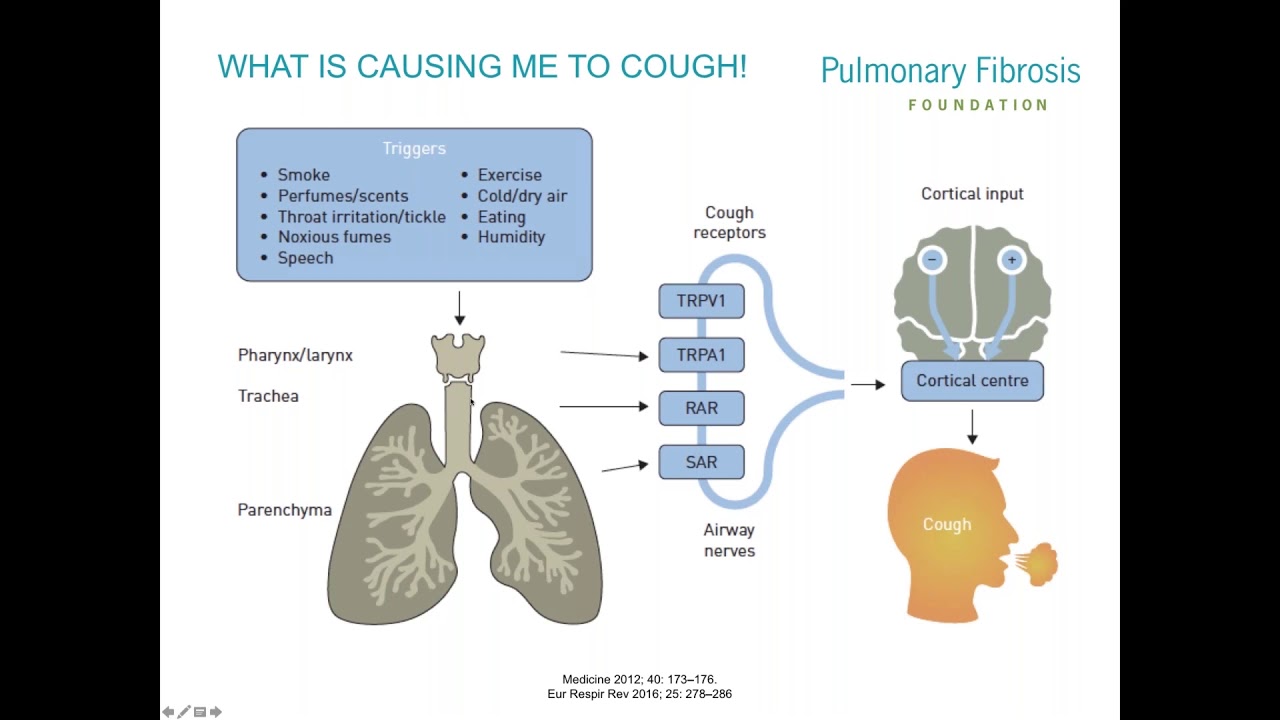
Children with epilepsy often experience seizures for a few minutes or longer. These episodes can cause uncontrollable jerking movements or blank stares. Seizures may occur in different parts of the brain depending upon their severity and cause. Because epilepsy is a condition that causes seizures to occur in different areas of the brain, it may be necessary for children to take multiple medications to treat them.
Genetic testing
The genetic testing of children with epilepsy can help to diagnose and treat the condition. This test can reveal if the child is affected by a disease-causing gene variant, which could explain why he or she has epilepsy. The physician can use the information obtained from the test to refine the treatment plan.
Families who are concerned about their child’s health can take the test. It can confirm the original diagnosis, reduce investigations, and provide additional information for family members. Besides confirming the diagnosis, genetic testing can also help physicians find other health problems associated with the child's epilepsy and determine the best course of treatment.
Medications
Medications for children's epilepsies can help control the seizures and prevent side effects. The dosage depends on the age and weight of the child. Depending on the severity of the seizures, the physician may recommend monotherapy or multiple medications. Children's epilepsy medications may need to change over time in order to avoid side effects or adverse reactions.
It is important to follow the recommended dosage and frequency for the medication. If a child is not taking the medication regularly, it could lead to side effects. Parents should talk with the school nurse to discuss their medication schedule. It is also important for parents to be aware of the side effects of different drugs.
Vagus nerve stimulator
A vagus nerve stimulator, or VNS, is an effective treatment for children with certain seizure disorders. This treatment is particularly effective for Landau–Klefner syndrome. However, other types of epilepsy might also benefit from it. Children under 12 years old may not be as well-suited than older children.

The vagus nerve stimulator works by sending small electrical pulses to the brain, helping the child to have fewer seizures. It is surgically implanted under the armpit or chest and attaches to the child's vagus nerve with a small wire. It can be activated automatically or manually to interrupt seizures.
FAQ
What are medical systems?
Medical systems have been designed to improve the quality of life and make it easier for patients to live longer and better lives. They ensure patients receive the best medical care, when and where they need it.
They ensure the best possible treatment at the right time. They also provide information that doctors need to be able to offer the best advice possible on the most appropriate treatment for each patient.
What should I know about immunizations?
Immunization is the process by which a vaccine stimulates an immune response. The body produces antibodies (immunoglobulins), to protect itself against infection after receiving the vaccine.
What are the three levels for health care facilities?
General practice clinics are the first level. They provide basic medical services to patients who don't require hospital admission. They may also refer patients to other providers if required. This includes nurse practitioners, general practitioners and midwives.
Primary care centers are the second level, which provide comprehensive outpatient care and emergency treatment. These include hospitals and walk-in clinics as well as urgent care centers.
The third level are secondary care centers, which offer specialist services such eye surgeries, orthopedic surgery, and neurosurgery.
Statistics
- Healthcare Occupations PRINTER-FRIENDLY Employment in healthcare occupations is projected to grow 16 percent from 2020 to 2030, much faster than the average for all occupations, adding about 2.6 million new jobs. (bls.gov)
- Over the first twenty-five years of this transformation, government contributions to healthcare expenditures have dropped from 36% to 15%, with the burden of managing this decrease falling largely on patients. (en.wikipedia.org)
- Consuming over 10 percent of [3] (en.wikipedia.org)
- The healthcare sector is one of the largest and most complex in the U.S. economy, accounting for 18% of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020.1 (investopedia.com)
- Foreign investment in hospitals—up to 70% ownership- has been encouraged as an incentive for privatization. (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
What are the 4 Health Systems
The healthcare system includes hospitals, clinics. Insurance providers. Government agencies. Public health officials.
The overall goal of this project was to create an infographic for people who want to understand what makes up the US health care system.
Here are some key points:
-
The GDP accounts for 17% of healthcare spending, which amounts to $2 trillion annually. It's nearly twice the size as the entire defense budget.
-
Medical inflation reached 6.6% last year, higher than any other consumer category.
-
Americans spend on average 9% of their income for health care.
-
There were more than 300 million Americans without insurance as of 2014.
-
Although the Affordable Care act (ACA) was signed into law, its implementation is still not complete. There are still significant gaps in coverage.
-
A majority of Americans believe the ACA should be maintained.
-
The US spends more than any other nation on healthcare.
-
The total cost of healthcare would drop by $2.8 trillion annually if every American had affordable access.
-
Medicare, Medicaid, as well as private insurers, cover 56% all healthcare expenditures.
-
These are the top three reasons people don’t get insured: Not being able afford it ($25B), not having enough spare time to find insurance ($16.4B), and not knowing anything ($14.7B).
-
There are two types: HMO (health maintenance organisation) and PPO [preferred provider organization].
-
Private insurance covers all services, including doctor, dentist, prescriptions, physical therapy, and many others.
-
The public programs cover outpatient surgery as well as hospitalizations, nursing homes, long term care, hospice, and preventive health care.
-
Medicare is a federal program providing senior citizens health coverage. It pays for hospital stays, skilled nursing facility stays, and home health visits.
-
Medicaid is a joint state-federal program that provides financial assistance to low-income individuals and families who make too much to qualify for other benefits.